Computer Organization and Architecture – Arithmetic and logic Unit (ALU)
Arithmetic and logic Unit (ALU)
ALU is responsible to perform the operation in the computer.
The basic operations are implemented in hardware level. ALU is having collection of two types of operations:
1.Arithmetic operations
2.Logical operations
Consider an ALU having 4 arithmetic operations and 4 logical operation.
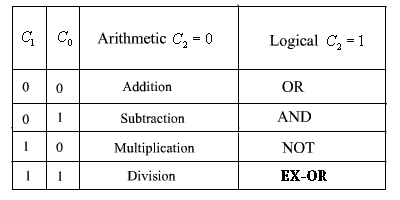
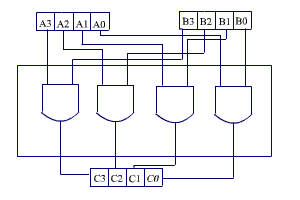
To identify any one of these four logical operations or four arithmetic operations, two control lines are needed. Also to identify the any one of these two groups- arithmetic or logical, another control line is needed. So, with the help of three control lines, any one of these eight operations can be identified.
Consider an ALU is having four arithmetic operations. Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Also consider that the ALU is having four logical operations: OR, AND, NOT & EX-OR.
We need three control lines to identify any one of these operations. The input combination of these control lines are shown below:
Control line is used to identify the group: logical or arithmetic, ie: arithmetic operation : logical operation.
Control lines and are used to identify any one of the four operations in a group. One possible combination is given here.
A decode is used to decode the instruction. The block diagram of the ALU is shown in figure below.
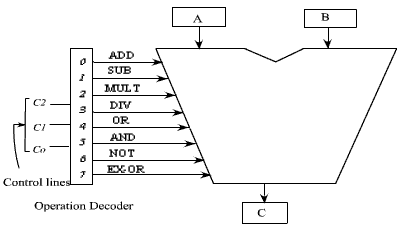
The ALU has got two input registers named as A and B and one output storage register, named as C. It performs the operation as:
C = A op B
The input data are stored in A and B, and according to the operation specified in the control lines, the ALU perform the operation and put the result in register C.
As for example, if the contents of controls lines are, 000, then the decoder enables the addition operation and it activates the adder circuit and the addition operation is performed on the data that are available in storage register A and B . After the completion of the operation, the result is stored in register C.
We should have some hardware implementations for basic operations. These basic operations can be used to implement some complicated operations which are not feasible to implement directly in hardware.
There are several logic gates exists in digital logic circuit. These logic gates can be used to implement the logical operation.
Some of the common logic gates are mentioned here.
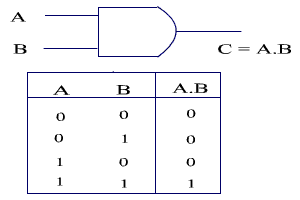
AND gate: The output is high if both the inputs are high. The AND gate and its truth table is shown in Figure below
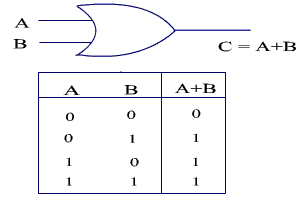
OR gate: The output is high if any one of the input is high. The OR gate and its truth table is shown in Figure below.
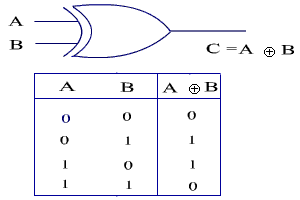
EX-OR gate: The output is high if either of the input is high. The EX-OR gate and its truth table is given in Figure below.
If we want to construct a circuit which will perform the AND operation on two 4-bit number, the implementation of the 4-bit AND operation is shown in the Figure below.
Arithmetic Circuit
Binary Adder :
Binary adder is used to add two binary numbers.
In general, the adder circuit needs two binary inputs and two binary outputs. The input variables designate the augends and addend bits; The output variables produce the sum and carry.
The binary addition operation of single bit is shown in the truth table
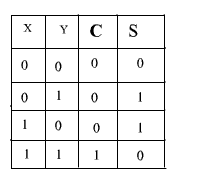
C: Carry Bit
S: Sum Bit
The simplified sum of products expressions are
![]()
The circuit implementation is
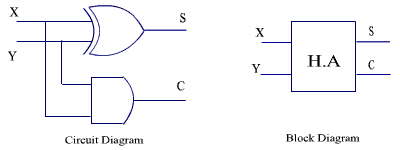
Figure : Circuit diagram and Block diagram of Half Adder
This circuit can not handle the carry input, so it is termed as half adder.The circuit diagram and block diagram of Half Adder is shown in Figure .
Full Adder:
A full adder is a computational circuit that forms the arithmetic sum of three bits. It consists of three inputs and two outputs.
Two of the input variables, denoted by x and y, represent the two bits to be added. The third input Z, represents the carry from the previous lower position.
The two outputs are designated by the symbols S for sum and C for carry.
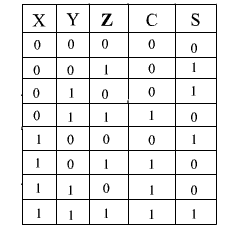
The simplified expression for S and C are
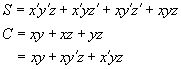
We may rearrange these two expressions as follows:
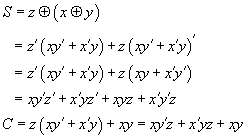
The circuit diagram full adder is shown in the figure.
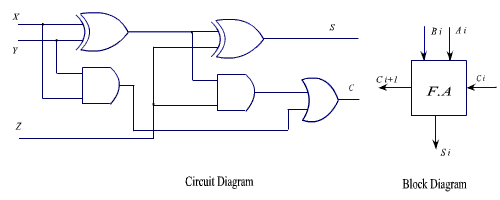
Figure : Circuit diagram and block diagram of Full Adder
The circuit diagram and block diagram of a Full Adder is shown in the Figure 2.7. n-such single bit full adder blocks are used to make n-bit full adder.
o demonstrate the binary addition of four bit numbers, let us consider a specific example.
Consider two binary numbers
A =1 0 0 1 B = 0 0 1 1
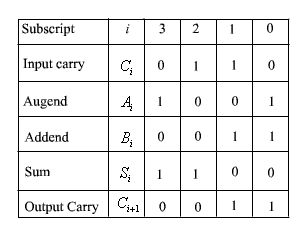
to get the four bit adder, we have to use 4 full adder block. The carry output the lower bit is used as a carry input to the next higher bit.
The circuit of 4-bit adder shown in the Figure below.
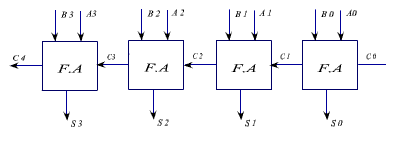
Figure : A 4-bit adder circuit.
Binary Subtractor :
The subtraction operation can be implemented with the help of binary adder circuit, because
![]()
We know that 2’s complement representation of a number is treated as a negative number of the given number.
We can get the 2’s complements of a given number by complementing each bit and adding 1 to it.
The circuit for subtracting A-B consist of an added with inverter placed between each data input B and the corresponding input of the full adder. The input carry must be equal to 1 when performing subtraction.
The operation thus performed becomes A , plus the 1’s complement of B , plus 1. This is equal to A plus 2’s complement of B .
With this principle, a single circuit can be used for both addition and subtraction. The 4 bit adder subtractor circuit is shown in the figure. It has got one mode ( M ) selection input line, which will determine the operation,
If M=0 , then A+B
If M=1 then A-B=A+(-B)
A+ 1’s complement of B+1
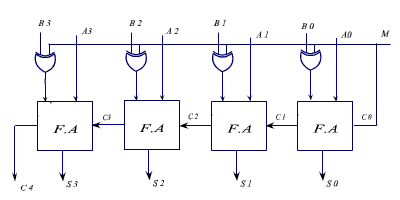
Figure : 4-bit adder subtractor
The circuit diagram of a 4-bit adder substractoris shown in the Figure .
The operation of OR gate:
![]()
![]()
![]()
For Offline Study you can Download pdf file from below link
Download Computer Organization and Architecture Arithmetic and logic Unit (ALU) PDF File