Programming in C – Common Functions In String

strcpy():
It is used to copy one string to another string. The content of the second string is copied to the content of the first string.
Syntax:
strcpy (string 1, string 2);
Example:
char mystr[10];
mystr = “Hello”; // Error! Illegal !!! Because we are assigning the value to mystr which is not possible in case of an string. We can only use “=” at declarations of C-String.
strcpy(mystr, “Hello”);
It sets value of mystr equal to “Hello”.
strcmp():
It is used to compare the contents of the two strings. If any mismatch occurs then it results the difference of ASCII values between the first occurrence of 2 different characters.
Syntax:
int strcmp(string 1, string 2);
Example:
char mystr_a[10] = “Hello”;
char mystr_b[10] = “Goodbye”;
– mystr_a == mystr_b; // NOT allowed!
The correct way is
if (strcmp(mystr_a, mystr_b ))
printf ("Strings are NOT the same.");
else
printf( "Strings are the same.");Here it will check the ASCII value of H and G i.e, 72 and 71 and return the diference 1.
strcat():
It is used to concatenate i.e, combine the content of two strings.
Syntax:
strcat(string 1, string 2);
Example:
char fname[30]={“bob”};
char lname[]={“by”};
printf(“%s”, strcat(fname,lname));
Output:
bobby.strlen():
It is used to return the length of a string.
Syntax:
int strlen(string);
Example:
char fname[30]={“bob”};
int length=strlen(fname);
It will return 3strchr():
It is used to find a character in the string and returns the index of occurrence of the character for the first time in the string.
Syntax:
strchr(cstr);
Example: char mystr[] = "This is a simple string"; char pch = strchr(mystr,‘s’); The output of pch is mystr[3]
strstr():
It is used to return the existence of one string inside another string and it results the starting index of the string.
Syntax:
strstr(cstr1, cstr2);
Example: Char mystr[]="This is a simple string"; char pch = strstr(mystr, “simple”); here pch will point to mystr[10]
String input/output library functions
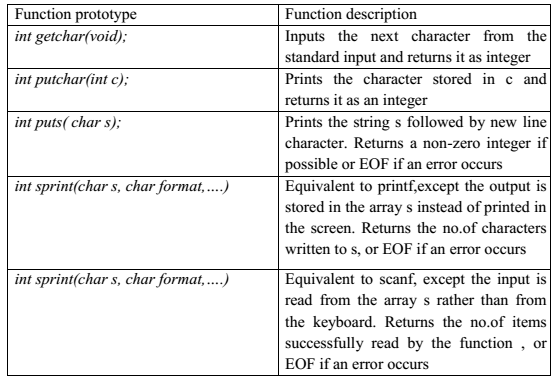
NOTE: Character arrays are known as strings.