Programming in C – Operators
An operator is a symbol that tells the compiler to perform specific mathematical or logical manipulations. C language is rich in built-in operators and provides the following types of operators:
• Arithmetic Operators
• Relational Operators
• Logical Operators
• Bitwise Operators
• Assignment Operators
• Increment and decrement operators
• Conditional operators
• Misc Operators
Arithmetic operator:
These are used to perform mathematical calculations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and modulus.
Following table shows all the arithmetic operators supported by C language. Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 20 then:


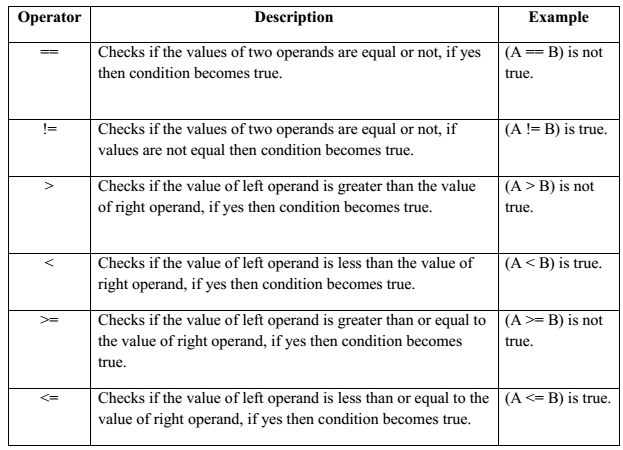
Relational Operators:
These operators are used to compare the value of two variables.
Following table shows all the relational operators supported by C language. Assume variable A holds 10 and variable B holds 20, then:
Logical Operators:
These operators are used to perform logical operations on the given two variables.
Following table shows all the logical operators supported by C language. Assume variable A holds 1 and variable B holds 0, then:

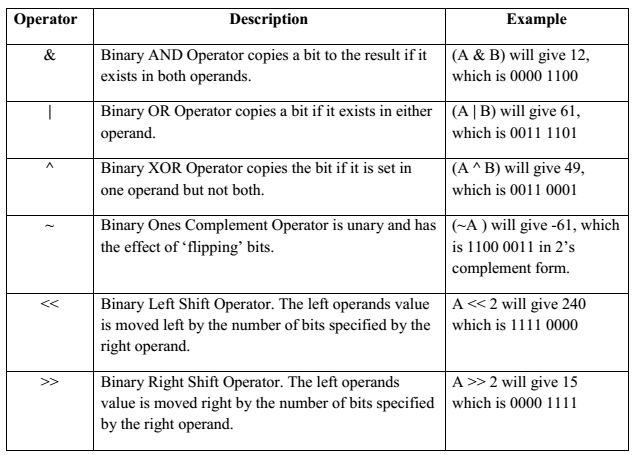
Bitwise Operators
Bitwise operator works on bits and performs bit-by-bit operation. Bitwise operators are used in bit level programming. These operators can operate upon int and char but not on float and double.
Showbits( ) function can be used to display the binary representation of any integer or character value
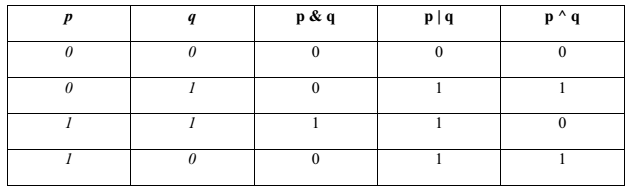
Bit wise operators in C language are; & (bitwise AND), | (bitwise OR), ~ (bitwise OR), ^ (XOR), << (left shift) and >> (right shift).
The truth tables for &, |, and ^ are as follows:
The Bitwise operators supported by C language are explained in the following table. Assume variable A holds 60 (00111100) and variable B holds 13 (00001101), then:
Assignment Operators:
In C programs, values for the variables are assigned using assignment operators. There are following assignment operators supported by C language: