Operating System – Disk files system management and optimization Long Questions Answers
 Here in this section of Operating System Long Questions and Answers,We have listed out some of the important Long Questions with Answers on Disk files system management and optimization which will help students to answer it correctly in their University Written Exam.
Here in this section of Operating System Long Questions and Answers,We have listed out some of the important Long Questions with Answers on Disk files system management and optimization which will help students to answer it correctly in their University Written Exam.Lists of Long Descriptive type Questions that may be asked in Written Exams.
- (1) Explain Disk files system management and optimization.
Question-1Explain Disk files system management and optimization.
Disk Space Management
- Files are normally stored on disk, so management of disk space is a major concern to file system designers.
- Two general strategies are possible for storing an n byte file:
- n consecutive bytes of disk space are allocated, or
- The file is split up into number of contiguous blocks.
- Storing a file as a contiguous sequence of bytes has the problem that if a file grows, it will probably have to be moved on the disk, for this reason all file systems divide files into fixed-sized blocks that need not be adjacent.
Block Size
- Having a large block size means that every file, even a 1 byte file, ties up an entire cylinder. It also means that small files waste a large amount of disk space.
- A small block size means that most files will span multiple seeks.
- Thus, if the allocation is too large, we waste space; if it is too small, we waste time.
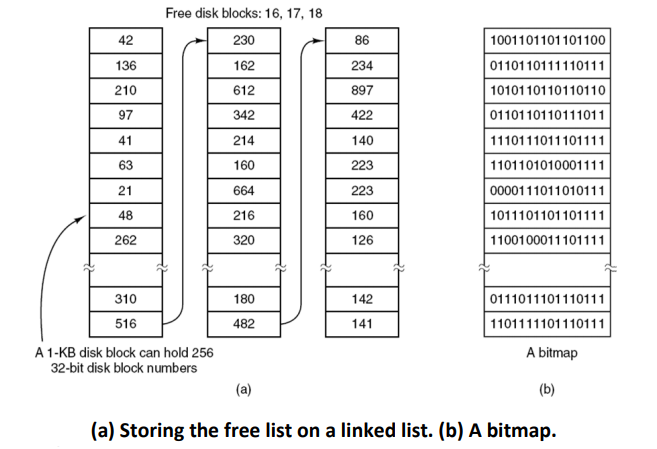
Keeping track of free blocks
- Once a block size has been chosen, the next issue is how to keep track of free blocks.
- Two methods are widely used
- First: Using a linked list of disk blocks, with each block holding as many free disks block numbers as will fit.
- Second: Bitmap – A disk with n blocks requires a bitmap with n bits. Free blocks are represented by 1s in the map, allocated blocks by 0s or vice versa.
- If free blocks tend to come in long runs of consecutive blocks, the free-list system can be modified to keep track of runs of blocks rather than single blocks.
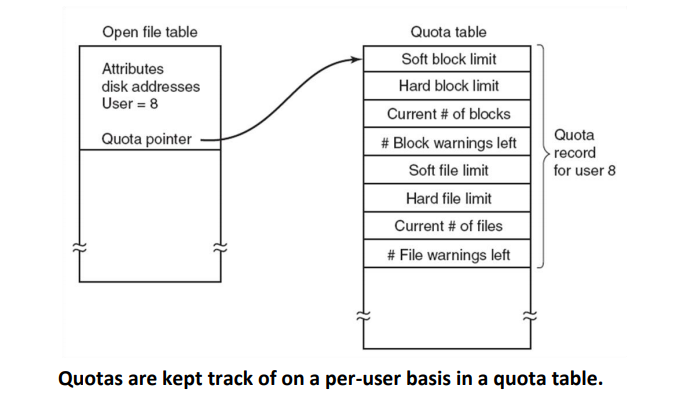
Disk Quotas
- The system administrator assigns each user a maximum allotment of files and blocks, and the operating system makes sure that the users do not exceed their quotas.
- Any increases in the file’s size will be charged to the owner’s quota.
- A table contains the quota record for every user with a currently open file, even if the file was opened by someone else.
- When all file are closed, the record is written back to the quota file.
- When a new entry is made in the open file table, a pointer to the owner’s quota record is entered into it, it make it easy to find the various limits.
- Every time a block is added to a file, the total number of blocks charged to the owner is incremented, and a check is made against both the hard and soft limits.